Depreciation is used to spread the cost of long-term assets out over their lifespans. Like amortization, you can write off an expense over a longer time period to reduce your taxable income. However, there is a key difference in amortization vs. depreciation. ABC Co. also determined the useful life of the intangible asset to be five years.
Example with Accumulated Amortization Account

Similarly, if a company has incurred an expense that has not yet been recognized, an adjustment entry is made to include this expense in the income statement. Intangible assets are non-physical assets that are used in the operations of a company. The assets are unique from physical fixed assets because they represent an idea, contract, or legal right instead of a physical piece of property. The journal entry is debiting amortization expense and credit accumulated amortization.
Amortization expense journal entry
Each entry consists of a debit and a credit, and is recorded in accordance with the double-entry accounting system. Amortization is important because it helps businesses recognize expenses in the appropriate accounting period. This has a myriad of benefits, including relevant financial reports that help investors, owners and other stakeholders make effective economic decisions. Need a simple way to keep track of your small business expenses? Patriot’s online accounting software is easy-to-use and made for small business owners and their accountants. When purchasing a patent, a company records it in the Patents account at cost.
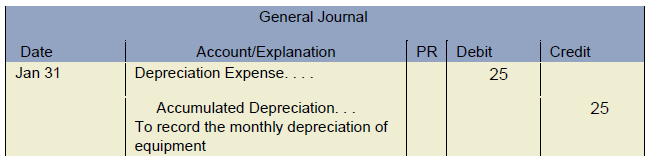
What are the journal entries for amortization expense?
ABC Ltd. purchased the business of XYZ Ltd. for a total of 50,000, while the actual book value of the business was 30,000. Show the journal entry for amortization of goodwill in the books of ABC LTD. in year 1 after the acquisition assuming it will be amortized over 10 years. Goodwill in accounting refers to the intangible value of a business that is above and beyond its tangible assets, such as equipment or inventory. It represents the reputation, customer base, and other non-physical assets contributing to the business’s value. Adjustment entries are an essential part of the accounting process. However, mistakes can happen, and it is crucial to avoid them to ensure accurate financial statements.
These standards require companies to accurately report their financial performance by recognizing and disclosing all relevant expenses. Intangible assets are purchased, versus developed internally, and have a useful life of at least one accounting period. It should be noted that if an intangible asset is deemed to have an indefinite life, then that asset is not amortized. This shifts the asset to the income statement from the balance sheet. Ensure that amortization expense is accurately recorded by reviewing the intangible asset’s useful life and estimated salvage value. Similar to the accumulated depreciation account, the accumulated amortization account can also be used to record the journal entry for amortization.
- Lastly, the credit to the cash or bank account is the amount of repayment made by the company.
- Intangible assets are non-physical assets that are used in the operations of a company.
- Sum-of-the-years digit amortization follows a curved pattern of cost distribution that increases over time.
- Another common circumstance is when the asset is utilized faster in the initial years of its useful life.
There are several steps to follow when calculating amortization for intangible assets. The four types of adjustments in accounting include accruals, deferrals, reclassifications, and estimates. Accruals and deferrals involve adjusting entries to record transactions that have occurred but have not yet been recorded. Reclassifications involve moving amounts between accounts, while estimates involve adjusting amounts based on expected future events. An example of an adjusting entry is the accrual of unpaid wages at the end of an accounting period.
They simply allocate the total cost of intangible assets from balance sheet to the expense on income statement. On the balance sheet, as a contra account, will be the accumulated which journal entry records the amortization of an expense amortization account. In some instances, the balance sheet may have it aggregated with the accumulated depreciation line, in which only the net balance is reflected.
Intangible assets appear after your current assets (liquid assets that can be quickly converted into cash) on the balance sheet. By providing transparency regarding asset usage and related costs, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to sound financial management practices. Amortizing lets you write off the cost of an item over the duration of the asset’s estimated useful life. If an intangible asset has an indefinite lifespan, it cannot be amortized (e.g., goodwill).


